Africa Francophone countries represent a unique cultural and linguistic community on the African continent. With a rich tapestry of history, culture, and diversity, these nations are bound together by the French language and shared colonial pasts. Understanding the significance of these countries is essential for anyone interested in African studies, linguistics, or global geopolitics.
In this article, we will explore the various facets of Africa Francophone countries, including their historical context, cultural richness, economic landscapes, and contemporary challenges. We will delve into the importance of the French language in these regions and how it influences education, politics, and social life.
Join us as we embark on this enlightening journey through Africa's Francophone nations, where we will uncover the beauty and complexities of a culturally vibrant part of the world. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply curious about global cultures, this guide will provide you with valuable insights and knowledge.
Table of Contents
- Historical Context of Francophone Africa
- List of Francophone Countries in Africa
- Cultural Diversity in Francophone Africa
- Economic Landscape of Francophone Countries
- Education and Language Policies
- Political Scenarios in Francophone Africa
- Challenges Faced by Francophone Countries
- Future Outlook for Francophone Africa
Historical Context of Francophone Africa
The historical roots of Francophone Africa can be traced back to the colonial period when European powers, particularly France, established colonies across the continent. The impact of colonialism is still evident today, influencing political structures, language, and cultural practices.
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, France expanded its colonial empire in Africa, acquiring territories that would later become modern-day Francophone countries. The legacy of this colonial rule has left a lasting imprint on the social, political, and economic landscapes of these nations.
Post-independence, many Francophone African countries struggled with the remnants of colonial governance, leading to political instability and economic challenges. Understanding this historical context is crucial for comprehending the current dynamics within these nations.
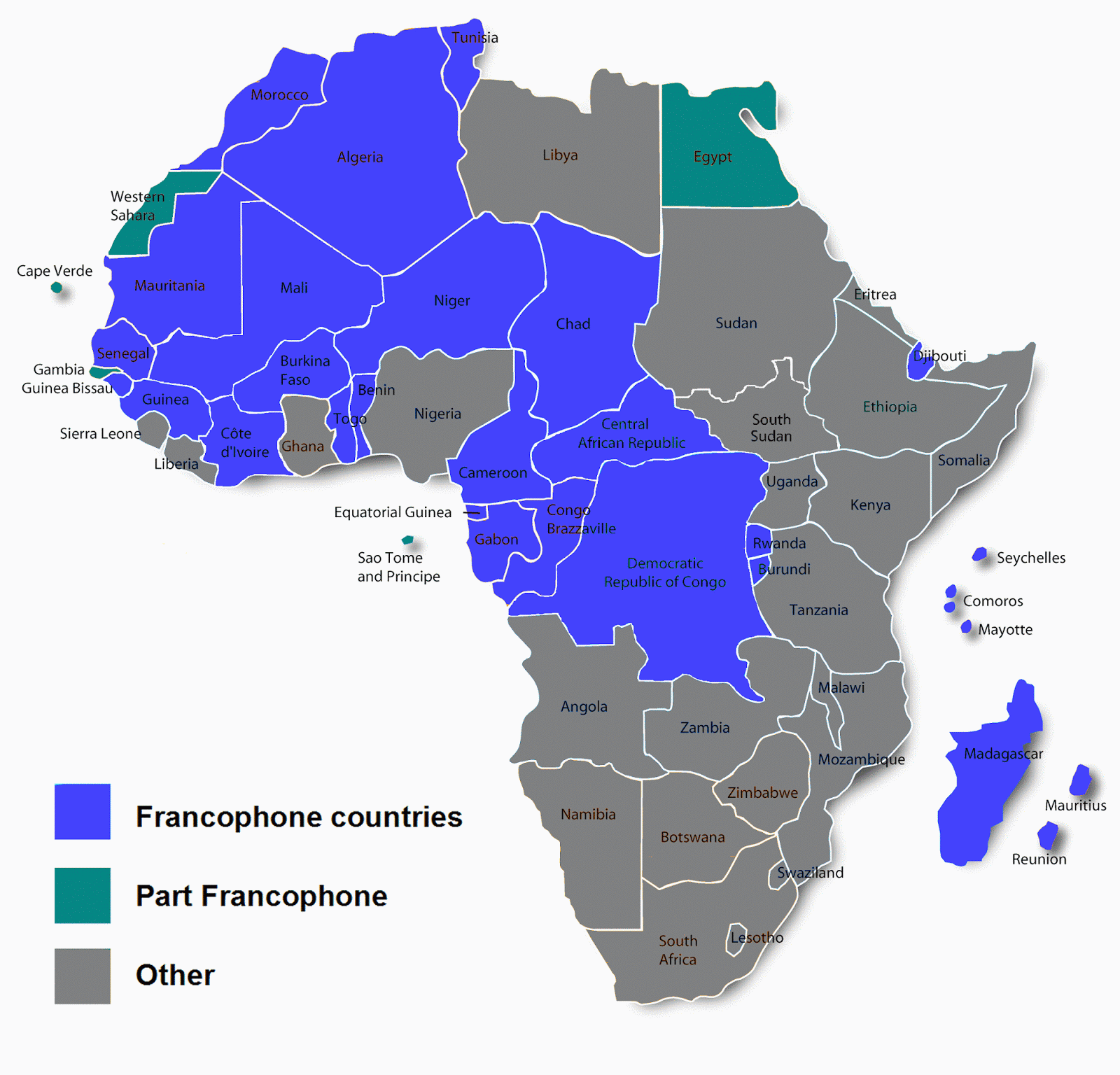
List of Francophone Countries in Africa
There are several countries in Africa where French is an official or widely spoken language. Here’s a list of these Francophone nations:
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cabo Verde
- Cameroon
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Equatorial Guinea
- France
- Gabon
- Guinea
- Ivory Coast
- Luxembourg
- Madagascar
- Mali
- Niger
- Rwanda
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Togo
Cultural Diversity in Francophone Africa
Francophone Africa is characterized by its immense cultural diversity, with each country possessing its own unique traditions, languages, and customs. While French serves as a unifying language, many local languages and dialects thrive alongside it.
For example, in countries like Senegal and Mali, the Wolof and Bambara languages play an essential role in daily communication and cultural expression. Festivals, music, and art often reflect the rich heritage of these communities, showcasing a blend of African and French influences.
Moreover, the culinary diversity in Francophone Africa is notable, with each region offering distinct flavors and cooking styles influenced by local ingredients and traditions.
Language and Identity
The French language in Francophone Africa is more than just a means of communication; it shapes national identity and cultural expression. It serves as a bridge connecting various ethnic groups and fostering a sense of unity.
However, the dominance of French has raised concerns about the preservation of indigenous languages and cultures. Efforts are being made to promote multilingual education and linguistic diversity to ensure that local languages are not overshadowed.
Economic Landscape of Francophone Countries
Economically, Francophone African countries exhibit a wide array of challenges and opportunities. Many of these nations are rich in natural resources, including minerals, oil, and agricultural products, which can drive economic growth.
However, issues such as political instability, inadequate infrastructure, and reliance on a single commodity can hinder development efforts. Countries like Gabon and the Democratic Republic of the Congo have vast natural wealth but face significant challenges in governance and resource management.
Investment Opportunities
Despite these challenges, there are emerging investment opportunities in sectors such as technology, agriculture, and renewable energy. The youth population in these countries presents a dynamic workforce that can contribute to innovation and economic progress.
International partnerships and investment are crucial for fostering sustainable development and building resilient economies in Francophone Africa.
Education and Language Policies
Education is a vital component of development in Francophone Africa. French is the primary language of instruction in many countries, which can create challenges for students who speak local languages at home.
Efforts to improve education systems are ongoing, with a focus on making learning more inclusive and accessible. Bilingual education programs that incorporate local languages alongside French are being implemented to enhance comprehension and retention.
Access to Education
Access to quality education remains a challenge in many Francophone African countries, particularly in rural areas where infrastructure is lacking. Initiatives aimed at improving access and quality of education are essential for empowering future generations.
Political Scenarios in Francophone Africa
The political landscape in Francophone Africa is diverse, with varying degrees of stability and democracy. Some countries have made significant strides toward democratic governance, while others face political turmoil and authoritarian regimes.
Countries like Senegal and Côte d'Ivoire have relatively stable political systems, whereas others, such as the Central African Republic, have experienced conflict and instability. Understanding the political dynamics in these regions is crucial for fostering peace and development.
Role of France and International Relations
France continues to play a significant role in the politics of Francophone Africa, often serving as a partner in development and security efforts. However, this relationship can be complex, with some countries expressing a desire for greater autonomy and less dependence on former colonial powers.
Challenges Faced by Francophone Countries
Francophone African countries face a myriad of challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and inadequate healthcare systems. These issues are often compounded by political instability and economic constraints.
Additionally, climate change poses a significant threat to agriculture and livelihoods in many of these regions, necessitating urgent action and adaptation strategies.
Social Issues
Social inequalities, particularly regarding gender and access to education, also remain pressing challenges. Empowering marginalized communities and promoting gender equality are essential for achieving sustainable development goals.
Future Outlook for Francophone Africa
The future of Francophone Africa holds both challenges and opportunities. With a growing youth population and increasing access to technology, there is potential for innovation and economic growth.
Investing in education, infrastructure, and sustainable development will be crucial for overcoming existing challenges and building resilient communities. Collaborative efforts at local, national, and international levels will play a vital role in shaping a promising future for Francophone African countries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Africa Francophone countries represent a vibrant and diverse region with a rich history and culture. While they face significant challenges, the potential for growth and development is immense. By understanding the complexities of these nations, we can appreciate their unique contributions to the global community.
We encourage our readers to engage with this topic further by leaving comments, sharing this article, or exploring more content related to Francophone Africa on our site.
Closing Thoughts
Thank you for taking the time to explore the fascinating world of Africa Francophone countries with us. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and knowledge. We invite you to return for more engaging content exploring global cultures and issues.