Generations shape societies, influence cultures, and define eras, making the study of generational cohorts a fascinating subject. In this article, we will explore the various generations, from the Silent Generation to Gen Z, and their unique characteristics, values, and impacts on the world. Understanding these generational cohorts can provide insights into societal trends, workplace dynamics, and cultural shifts.
As we delve into the list of generations, we will uncover what defines each group, how their experiences have shaped their perspectives, and the implications for future generations. This knowledge is essential for marketers, employers, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the evolving landscape of society.
Join us as we embark on this journey through time, examining the distinct traits of each generation and how they contribute to the rich tapestry of human history.
Table of Contents
- Silent Generation (1928-1945)
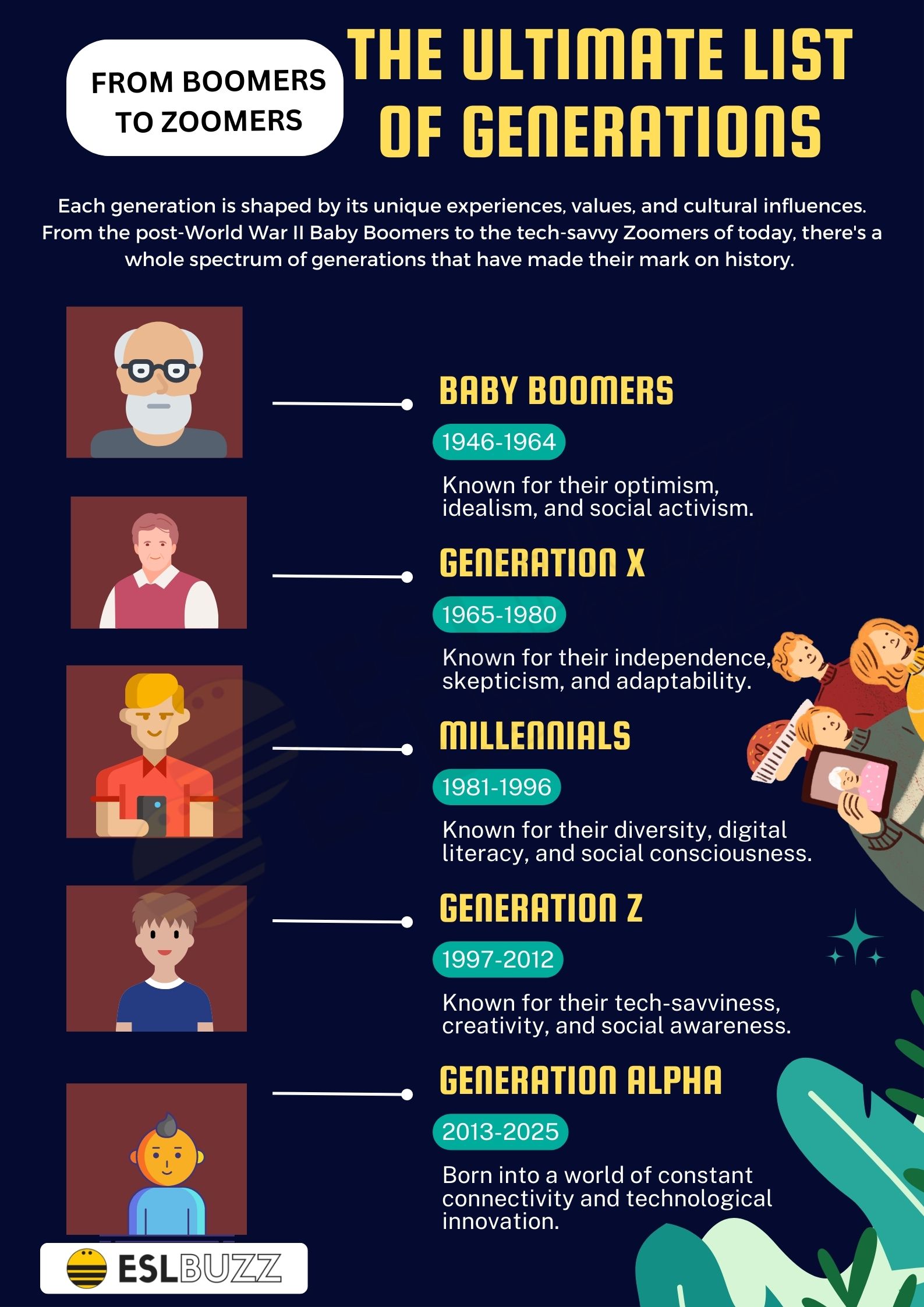
- Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
- Generation X (1965-1980)
- Millennials (1981-1996)
- Generation Z (1997-2012)
- Generation Alpha (2013-Present)
- The Impact of Generations on Society
- Conclusion
1. Silent Generation (1928-1945)
The Silent Generation, born between 1928 and 1945, is characterized by traditional values and a strong work ethic. This generation experienced significant events such as the Great Depression and World War II, which influenced their outlook on life.
- Key Characteristics:
- Value hard work and loyalty.
- Typically conservative and risk-averse.
- Strong focus on family and community.
- Notable Figures:
- Martin Luther King Jr.
- John F. Kennedy
- Julia Child
2. Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
Baby Boomers, born from 1946 to 1964, are known for their significant impact on culture and economy. This generation came of age during a time of social upheaval, leading to movements such as civil rights and feminism.
- Key Characteristics:
- Value personal gratification and ambition.
- Experience with technological advancements.
- Highly competitive in the workplace.
- Notable Figures:
- Bill Gates
- Oprah Winfrey
- Elon Musk
3. Generation X (1965-1980)
Generation X, often referred to as the "middle child" generation, was born between 1965 and 1980. They are known for their adaptability and independence, having witnessed the rise of technology and economic uncertainty.
- Key Characteristics:
- Value work-life balance.
- Highly skeptical of authority.
- Embrace diversity and inclusivity.
- Notable Figures:
- Barack Obama
- Rihanna
- Leonardo DiCaprio
4. Millennials (1981-1996)
Millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, are known for their tech-savvy nature and desire for meaningful work. This generation has been shaped by the internet and social media, leading to a unique approach to communication and connection.
- Key Characteristics:
- Value collaboration and teamwork.
- Focus on social issues and sustainability.
- Seek work that aligns with personal values.
- Notable Figures:
- Mark Zuckerberg
- Emma Watson
- Greta Thunberg
5. Generation Z (1997-2012)
Generation Z, the cohort born from 1997 to 2012, is the first generation to grow up with smartphones and social media as a norm. This generation is marked by their digital fluency and social awareness.
- Key Characteristics:
- Highly connected and socially conscious.
- Advocate for mental health awareness.
- Value authenticity and transparency.
- Notable Figures:
- Billie Eilish
- Malala Yousafzai
- Finn Wolfhard
6. Generation Alpha (2013-Present)
Generation Alpha, born from 2013 onwards, is the youngest generation and is still developing. They are expected to be the most technologically immersed generation yet, growing up with AI and advanced technology.
- Key Characteristics:
- Expect seamless technology integration.
- Open to diverse forms of education.
- Potentially more globally minded due to access to information.
7. The Impact of Generations on Society
The interplay between generations has a profound impact on culture, politics, and the economy. Understanding these dynamics can help navigate societal changes and foster intergenerational collaboration.
- Social Change:
- Each generation has contributed to significant social movements.
- Generational differences shape political ideologies.
- Workplace Dynamics:
- Understanding generational characteristics can improve team collaboration.
- Employers can tailor engagement strategies to attract diverse talent.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the list of generations provides valuable insights into societal trends, cultural shifts, and workplace dynamics. From the Silent Generation to Generation Alpha, each cohort has unique characteristics and influences that shape our world today. As we move forward, recognizing and appreciating these differences will be crucial for fostering collaboration and innovation in an ever-evolving society.
We invite you to share your thoughts in the comments below and explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of generational dynamics!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again soon!

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/names-of-generations-1435472_v31-5b48e0cec9e77c0037f56645.png)

